Disclosure: Privacy Australia is community-supported. We may earn a commission when you buy a VPN through one of our links. Learn more.
Cryptocurrency Master Guide: Turning Digital-Coin Curiosity Into Long-Term Knowledge
Cryptocurrencies have taken the world by storm, leading millions of people down the crypto rabbit hole of blockchains and distributed ledger technology.
Now if that sounds a bit daunting, rest assured that the following guide will help you transition to the small group of people who fully comprehend how cryptocurrencies operate. After all, the mainstream popularity which surrounds this movement is not a coincidence.
On the contrary, governments and large corporations are paying close attention to digital currencies due to their innovative ability to solve the problem known as double-spending. Additionally, this system undermines the long-lasting centralized arrangement where entities such as banks are able to enact a market monopoly and thus charge high fees for their “middlemen” services.

So, to explain it vaguely, cryptocurrencies are a new generation of digital currencies that are secured through a peer-to-peer network. There is, of course, a lot more information that one must understand to get a solid grasp of things like Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum, and so on. If you already know all this, you might be interested in the newest blockchain use cases.
The Innovation and Crypto-Based Software
One of the first things many users ask pertains to the actual name of cryptocurrency.
The reason why it carries the “crypto” part of its name is due to the system which secures it. Cryptocurrency is a decentralized system where all transactions are protected by cryptography, which is a way of transmitting data in a form that will be unintelligible to all users besides the intended recipient and the original sender. Meaning, it is a way to convert ordinary files into encrypted ones that can only be accessed by the authorized few that meet the specific requirements to do so.
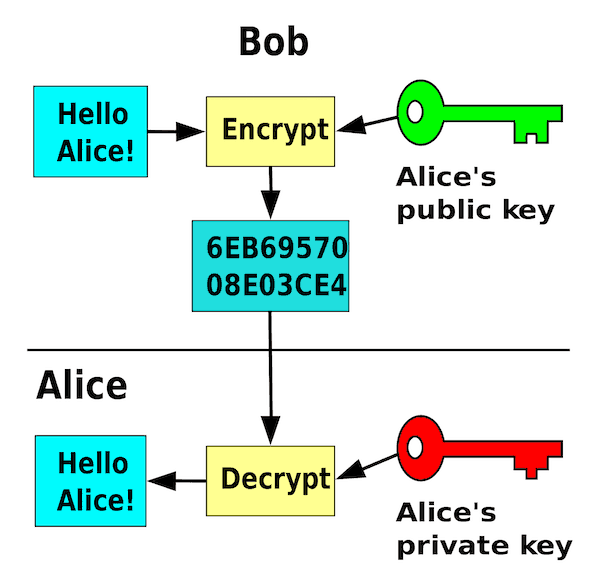
The most obvious explanation as to why cryptocurrencies have taken off and become a great alternative to ordinary centralized systems are the benefits they offer. Some of those are, but not limited to, confidentiality, integrity, speed, and much more.
Below is a detailed analysis of some of the most important factors you should consider before we get into the ins and outs of blockchain and mining.
Accessibility – Unlike a lot of centralized systems, cryptocurrency is accessible to everyone. Consider, for instance, how most banking systems operate. In order to open an account, intermediaries will analyze things like personal income, credit score, employment history, and so on.
Then, they will decide whether the candidate qualifies for the account. Cryptocurrency removes such steps from the procedure and openly invites everyone to become a user.
Universal Recognition – Besides allowing people to own cryptocurrency without a ton of mind-boggling requirements, it also provides them with a database recognized around the world.
Unlike traditional currencies, digital ones are not bound by volatile exchange rates that fluctuate daily, interest rates, incoming transaction fees that countries may put in place for international transfers, and much more.
Just consider the fact that all currencies in the world can be adversely impacted by nearly all political and social events. Cryptocurrency, on the other hand, is immune to such spikes as globalization-based events will not cause its value to plummet nor shoot upward. This is not true of regulation, however, and we will later showcase what some countries are doing to address this new network.
Reduced Fees – Cryptocurrency blockchains are expanded by people known as miners. Fortunately for the users, all mining is covered by the platforms themselves. Meaning, the users are never going to lose their digital coins by paying for confirmation fees. With banking institutions, however, that is not the case.
After all, the way that banks make money is through interest rates, transaction fees, and a lot of other perpetual charges that users have to pay on an on-going basis. This is another area where cryptocurrency is dominating the sector as it significantly reduces the outstanding fees for making transactions.
Sender-Based – When you use a debit or a credit card to pay for something, the seller deducts an amount from your account based on the price they offer. That means that the payment system is based on seller-initiated transactions where they dictate the amount which will be taken out of the database or your account in this case.
Cryptocurrency puts the control back into the hands of the buyer. Instead of letting the seller dictate the amount, the buyer is the one that chooses how many coins they will transfer. To ensure additional security is provided, every transaction must be initiated with a private key. Only then will the funds be transmitted to the buyer.
The Person Behind It All: Meet Satoshi Nakamoto!
It all started with Bitcoin. By now, you have probably heard of it due to its booming price in 2017, amazing abilities praised by countless investors, or simply via one of the innumerable news channels that took time to report on it. In reality, if there was ever anything close to a “pioneer” of the entire cryptocurrency movement, it would be Bitcoin.

It originated in 2009 when an unidentified person or group of people going by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto introduced it. Nakamoto used something known as the SHA-256, a set of NSA-developed cryptographic hash functions, as its proof-of-work consensus algorithm that is used to confirm new blocks to the chain. A few years later, others followed suit and we saw Namecoin and Litecoin come about in 2011.
As of March 2018, almost a decade after Nakamoto paved the way for cryptocurrencies around the world, there are as many as 1,658 of them in existence.
Besides permanently changing the landscape of centralized currency systems, Satoshi Nakamoto caused a lot of positive disruption in many other industries. For example, decentralized currency systems are in direct competition with intermediaries like large banking institutions. But the consequences of a successful blockchain technology system that was created are much more far-reaching.
In fact, when developed correctly, blockchain systems could undermine almost all other intermediaries in the world. That includes the streaming platform where you might be listening to your top music artists, the online stores where you might be purchasing your phone apps, and even e-mailing websites where you might go to send and receive messages.
Just consider companies like:
- Yahoo
- Spotify
- Dropbox
- Visa
One of the many things that all of them have in common is their middlemen-based nature. Spotify, per se, runs their subscription network by putting artists’ work in front of the audience that streams it. Similarly, Dropbox provides a digital platform where pre-made files can be dropped off and shared with others. Meaning, they all serve the public by providing an outlet where the supply and demand are matched based on a lot of predetermined factors.
Well, this is where cryptocurrency enters the scene. Instead of relying on third parties that require perpetual fees in exchange for access, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin connect users directly with one another. Behind an ocean of coding that protects private information, the blockchain system removes the middlemen so that two strangers can directly transact with each other.
What Exactly is Double-Spending?
One of the main reasons why digital coins were unsuccessful in the past comes from their inability to prevent a phenomenon known as double-spending. If you never heard about the term before, it is because all of your transactions so far have been protected by those third-parties known as intermediaries in a centralized system.
With digital currencies, however, the system of operations is decentralized.
That means that it is primarily controlled by the users without an authoritative figure that can verify all transactions and consequently stamp their seal of approval. Well, one of the main reasons why Satoshi Nakamoto’s Bitcoin was so successful is the fact that it efficiently solved the double-spending problem that many others failed to address.
Before explaining how this was achieved, however, let us take a closer look at double-spending and define what it is.
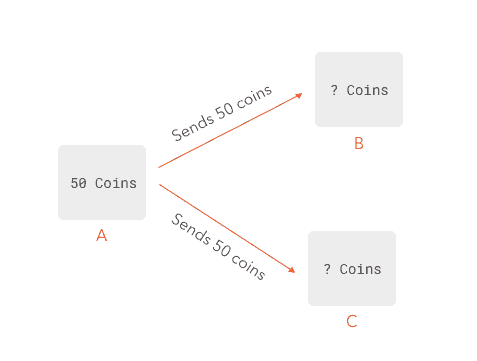
Double-spending is a threat to digital coin schemes in which any given coin or token can be used more than once. To better understand the concept, you should see all digital currencies as nothing more than computer files. And as you may know, all computer files can be easily copied and pasted.
Just think of all the times you moved something from one folder to another with a quick control-plus-C and control-plus-V function.
So, the problem arises because digital tokens can be copied and cause terrifying issues such as a rise in inflation due to a fraudulent currency that did not previously exist.
Consider the following real-world example:
If you own some digital currency valued at $100, you get to use it for purchasing goods or services in that amount at your discretion. But what happens when your file that contains the value is copied and fraudulently used? Ultimately, it leads to a reduction in the credibility of the digital currency and destroys all trust that was previously built.
Not anymore.
Bitcoin put an end to this concern by enacting something known as a peer-to-peer system and a chronologically-ordered ledger that is updated every ten minutes. Instead of having a central authority like a large bank that views and approves the transaction, every Bitcoin user fulfills this role.
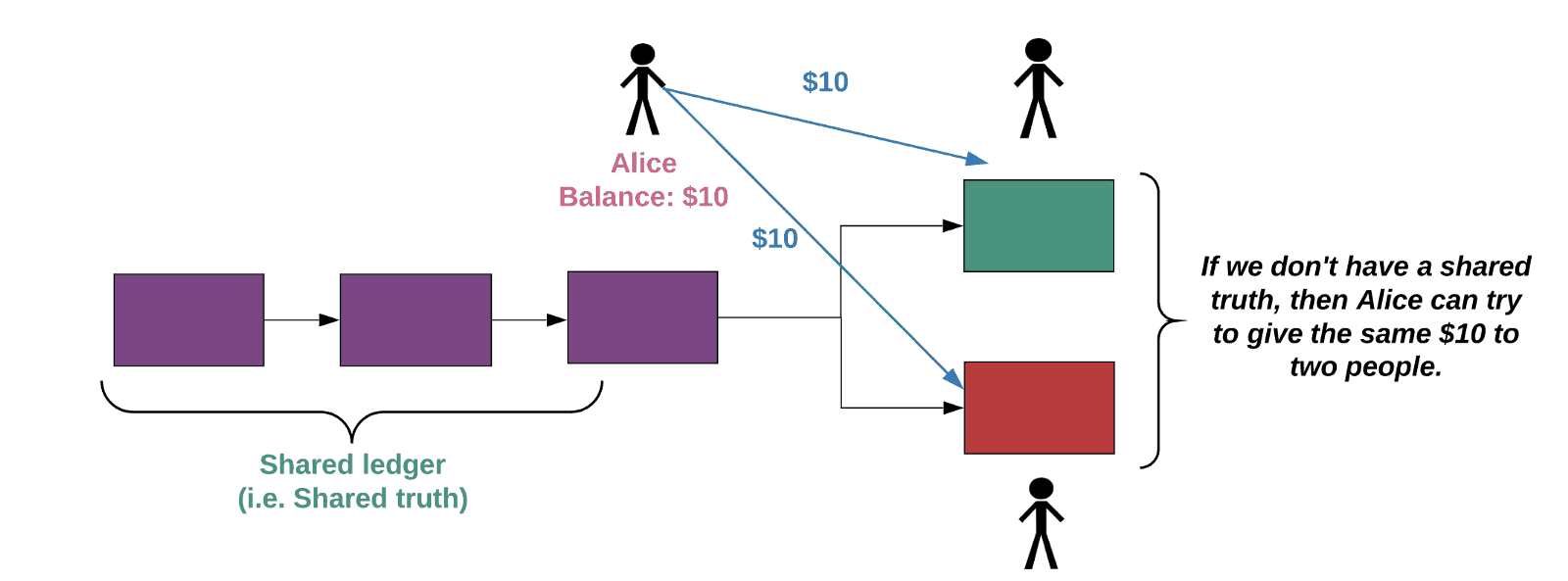
In simple terms, every user has a copy of the public ledger where transactions are recorded. Additionally, all account balances are made public while personal information remains hidden for user privacy. Once a transaction is initiated, all peers must achieve a consensus or the transaction will be neglected. Below is a good way to portray how a real-life example would work:
To further protect your online privacy, we recommend first hiding your IP address. Furthermore, you can do that and apply many other security measures by getting some of the best VPN services out there.
Imagine five different users that have cryptocurrency.
For the purposes of this scenario, we can call them Q, X, Y, Z, and W.
Now let us assume that X wants to send some currency to Y.
First, X will initiate the transfer with their private key.
Then, all five users will receive information about the transaction that will be displayed on their public ledger. If all five peers have matching information, the transaction will be confirmed and permanently entered into the system through mining.
But what happens if somebody tries to initiate a fraudulent transaction? This is where Nakamoto’s innovative solution comes in. Whenever a blockchain copy of a transaction does not match all of the other users’ ledgers, it is automatically rejected.
So, let us say that user X is attempting to fraud someone.
First, they will be unable to do so due to their blockchain copy being different from what all other users have. Then, the system will be able to pinpoint them as the party that attempted to initiate a fraudulent transaction because they will be the only one with a different blockchain copy in the entire system.
Confirmation as the Essence of Cryptocurrency Systems and the Role of Miners
When a transaction is initiated with a user’s private key, it needs some time to be confirmed. Until that happens, it is marked as pending. Metaphorically speaking, the confirmation can be viewed as the Sun around which the planet of cryptocurrency revolves.
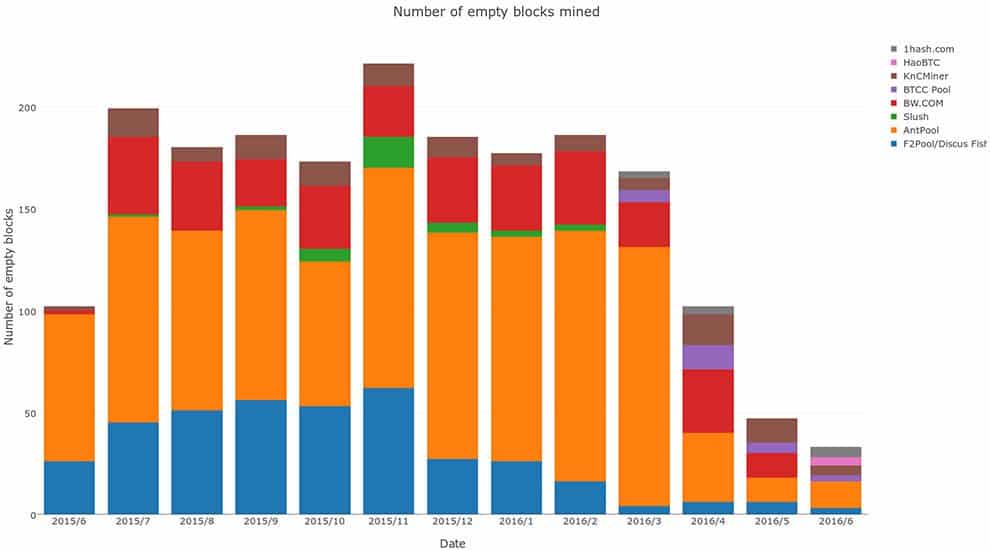
This is because bitcoin confirmations are the only way that a new transaction will get spread to the rest of the network. Once that happens, every user will add it to their database and it will become an everlasting part of the system that can never be removed. So, how do confirmations happen?
What is Blockchain Mining?
In the case of Bitcoin and most other digital currencies, for example, mining is the only way to add additional blocks to the chain. It is also a way for somebody to own Bitcoin without having to buy it with fiat money like the United States Dollar, Euro, and so on. In simple terms, it is the process by which miners solve complex mathematical puzzles and perform a role of modern-day auditors. However, it is possible to buy Bitcoin anonymously, if you do a bit of research.
For those unfamiliar, auditors are certified accountants that verify corporate financial statements to ensure their validity and accuracy so that potential investors would not be scammed by false information. With cryptocurrency, however, miners fulfill a role of verification where they go through previous transactions and ensure that they are valid.
That means that they prevent any fraudulent activity and make sure that the users are remaining honest.
In return, they get paid in Bitcoin for the work performed.
In fact, the way miners get paid is the only way to release new coins to the market.
Currently, miners earn 12.5 Bitcoin for completing a block. Although the value fluctuates, as of June in 2018, that fee will earn them an $84,212 as the value of one coin is $6,737. Additionally, the current supply of Bitcoin released to the market is 17.1 million. The reason why that matters is that the Core Money Supply of this cryptocurrency will be capped at 21 million.
Meaning, there will be no more Bitcoin released once the aforementioned market cap is reached. For miners, this is an extremely important piece of information as it affects the amount that they will be compensated for completing a “confirmation” of a transaction and adding a new block to the chain.
Originally, when Bitcoin first started operating, miners would receive 50 coins for every block that they added to the chain.
After a while, in 2012, that reward went down to 25 coins to slow down the rate at which coins were getting released to the market. In 2016, the reward was reduced by a half to 12.5 coin, and in 2020 it halved again and currently stands at 6.25 coins. According to the Bitcoin Clock, the reward for miners will fall down to 3.125 coins in 2024. This event occurs every 210,000 blocks, roughly every four years.
Other cryptocurrencies operate in a similar manner. In fact, all that needs to be done to create new digital currency is for someone to slightly alter the original code that Satoshi Nakamoto wrote. Then, once the code is changed and somehow optimized or improved for a different purpose, a new cryptocurrency is formed.

Take Litecoin for example. It came in 2011 when the Bitcoin code was slightly changed to be able to process more payments in less time. Nevertheless, the miners that operate with Litecoin have the exact same role. They verify transactions based on solving large and complex puzzles. Once they do so, they are compensated in Litecoin.
Lastly, it is important to look over some of the current issues that cryptocurrency miners are facing. Arguably, the most important one deals with the environmental effects of mining. Although the entire process is extremely complicated and requires high-level mathematical and coding skills, it also requires tangible assets in order to mine.
In translation, one must have an unbelievably strong system and be ready to utilize a ton of electricity. According to some calculations, the current energy use for Bitcoin stands at around 70 terawatt-hours per year. To put this in a life-like example, such numbers indicate that Bitcoin miners are using more electricity than the entire Czech Republic.

Pictured above: A lot of horsepower
Expectedly, such absurd requirements are raising questions about the long-term capabilities of cryptocurrencies. Luckily, cryptocurrency miners are in the business of making a profit. If they are forced to spend thousands of dollars to simply cover the electricity for their venture, they will have less money to keep.
That is why a lot of them are turning to renewable energy sources that enable them to minimize spendings while also protecting the environment. In fact, there are plenty of vivid comparisons that demonstrate how Bitcoin mining is nowhere near the annual economic cost that the banking systems, per se, come with.
Shockingly, the banking systems are actually spending over 2,300 times more than cryptocurrency miners.
Besides environmental impacts, another current issue that relates to mining concerns the platforms which are used to mine. On June 12 of 2018, Apple came out and openly banned all mining that used to be done utilizing iPhones. Miners will no longer have access to apps that allow them to do their job as Apple changed the developer guidelines and made it impossible to create mining-capable apps while terminating the existing ones.
Once again, however, this issue yields a little-to-no negative impact on existing cryptocurrency miners.
Why?
Because it is highly unlikely that anyone would be able to do something as sophisticated as blockchain mining on a mobile device.
Regardless of the power that Apple equips their iPhones with, it is nowhere near the necessary level of performance to do transaction confirmations. Instead, users will have to continue using very special computers that are formally known as “rigs“.
What is the Cryptocurrency Store of Value?
Now that you know what cryptocurrencies are and how transactions are created, confirmed, and additional coins released to the market, it is time to look at the entire discussion from another angle.
Namely, cryptocurrencies are also very important as a worldwide store of value.
Although their primary use revolves around making payments for goods and services directly to the sellers, they are a promising investment. Consider, for example, the way Bitcoin traveled from its initial value, which was established with a “Genesis Block” in 2009, to a staggering $69,000 per coin towards the end of 2021.
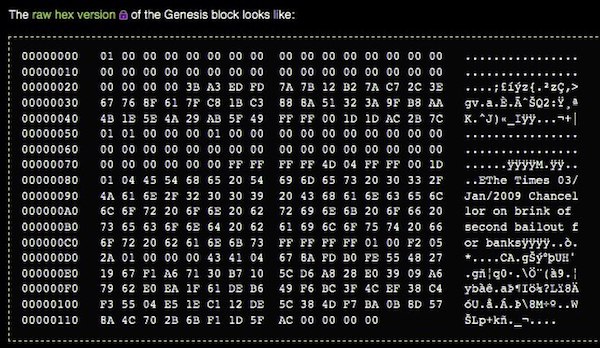
For clarification purposes, the Genesis Block is the very first block ever created. Every other block was subsequently entered through mining and remaining coins were released to the market in form of direct purchases or miners’ fees.
So, if an unsuspecting investor was to purchase a single coin back in 2010, per se, they would have paid around six cents for it.
Then, let us assume that they kept the coin until December of 2021. Doing so would effectively earn them more than $60,000 as the value went up beyond anyone’s expectations. So, it is very obvious that Bitcoin can be viewed as a powerful store of value. Not so much for the others. Aforementioned Litecoin for example, keeps losing value when compared to Bitcoin.
Similar to currency traders that make money by buying countries’ currencies while they are weak and re-selling them when they get stronger, digital coins can be traded effortlessly on many markets. Just in the past 24 hours, the exchange volume that took place on 198 most popular crypto markets is 3.86 billion dollars.
This indicates that the store of value power that cryptocurrencies carry is not a bold statement. On the contrary, it is a fact proven by an on-going track record of high-volume exchanges that are continuously making successful investors even more profitable.
You can store your personal cryptocurrencies using both digital crypto wallets, and using crypto paper wallets, which are even more fun to learn about.
Bitcoin: The Begining of Cryptocurrency
Even though Bitcoin remains the most popular cryptocurrency with the largest market cap, it seems to be just the start of a powerful movement that has already dominated the economic landscape for some time. Naturally, after it came under the spotlight many years ago, a lot of other digital coins were created with the intention to capture a portion of its success.
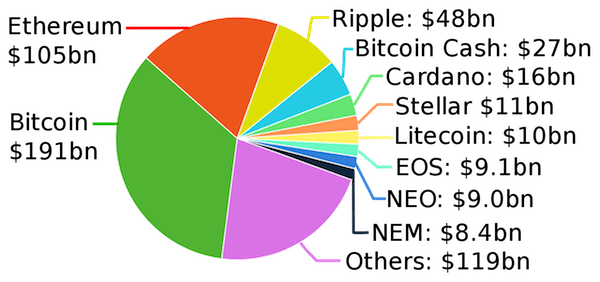
Some of them, which were previously introduced, include Litecoin and Ethereum. Thus, it is important to note that Bitcoin was just the beginning of something that may soon take over the world’s economy. To better understand such a bold claim, take a look at the following analysis of a few different cryptocurrencies that are gaining momentum and operate in a slightly altered way from Bitcoin yet use the same blockchain-style technology.
Ripple Cryptocurrency
Co-founded by Chris Larsen and Jed McCaleb, the creator of MtGox, in 2012, Ripple is a popular cryptocurrency as well as a payment system. In reality, the vast majority of its mainstream popularity comes from a peer-to-peer-based, decentralized payment protocol that offers all the benefits of direct transfers that can be done with every form of money.

The piece of code that effectively differentiates Ripple from Bitcoin, however, pertains to the proof-of-work system. Unlike most other cryptocurrencies, this system takes advantage of trusted gateways that act as middlemen.
A user can initiate a transaction using a specific gateway that will submit the funds to the recipient’s gateway. Then, the recipient needs to satisfy a set of criteria to release the funds from the gateway and take possession. To avoid the notorious issue known as double-spending, there is a consensus protocol.
Thus, if someone tries to send the same funds via multiple gateways, the system will only accept the first transaction as it will receive the most confirmations that are issued approximately five seconds after the transaction started.
Litecoin Cryptocurrency
The next, and somehow poor alternative to Bitcoin is Litecoin. It was created by a Google engineer Charles Lee in 2011 who modified the code in order to reduce the time it takes to mine blocks. Some of the major differences are related to the algorithm type, mining rewards, and market caps.

First, unlike Bitcoin that uses an SHA-256 algorithm, Litecoin takes advantage of Scrypt hash function with intensive memory. So, although nearly 200 trillion hash computations are performed by the second, the Random Access Memory (RAM) always stores the numbers. Ultimately, the bottom line factor that separates Litecoin from Satoshi Nakamoto’s creating is the mining speed.
As previously discussed, the mining process for Bitcoin yields a new block every ten minutes. Well, Litecoin reduces this by four times and makes it possible to add blocks every two and a half minutes.
Additionally, the rewards for successful mining with Litecoin are halved every 840,000 blocks, which is four times more than the rate at which Bitcoin halves their mining rewards. It is important to note, however, that this cryptocurrency is currently valued hundreds times less than Bitcoin and the gap is only getting bigger over time.
Ethereum Cryptocurrency
Lastly, one of fastest-growing “alternatives” to Bitcoin is Ethereum. The problem with that claim, however, is the fact that Ethereum is not an alternative whatsoever. Instead, it can be looked at as a platform where many other blockchain applications are developed.

So, if Bitcoin is viewed as a single e-mail on a server, Ethereum acts like the entire platform that helps create those e-mails. To better understand this, let us define Bitcoin as nothing more than what it can do at present time – a user-to-user cash system that allows digital coin transactions. Although the innovation required to achieve something so sophisticated is beyond most people, it only showcases a small range of possibilities.
In fact, blockchain technology is capable of creating decentralized systems with a proof-of-work approach in countless industries. This is where Ethereum grabs the spotlight. It was originally released in July of 2015 and operates via something called smart contracts.
Simply put, those contracts are codes that guarantee a transfer of funds once specific requirements are satisfied. The payment is done using the network’s own store-of-value coin called Ether. This is where users take advantage of Ethereum’s powerful Turing complete software better known as Ethereum Virtual Machine. The cryptocurrency switched from Proof of Work algorithm to Proof of Stake, making it less decentralized in the long run, similar to aforementioned Ripple.
It is a program that can develop countless applications via blockchain technology within the network.
Meaning, developers use smart contracts to create new apps based on decentralized, peer-to-peer systems which, when executed, trigger the contract’s fulfillment and pay the developers in Ether. Furthermore, if you want to know how to become a blockchain developer, we have prepared a guide just for you.
How Long Will Cryptocurrency Last?
As with any long-term venture and investment, the ultimate goal tends to be profitability intertwined with longevity. Fortunately, cryptocurrency seems to be one of the few inventions that are here to stay.
Ignoring the value rollercoaster, which will be mentioned shortly, we must note the potential that digital currency comes with as the world moves closer to global modernization. It presents a way to sidestep intermediaries in almost all industries by taking advantage of a network that operates outside of any central authority’s reach. Consequently, such frame makes it very probable that governments around the world will get involved, if they have not already.
What is Happening With Cryptocurrency Regulations?
One of the most obvious happenings in the future of cryptocurrency is regulation. The fact that there is no central backing of digital currencies makes regulatory bodies worry. Hence why we can assume that many heated debates are to follow as these assets keep growing in popularity and market power.
For example, the United States already took some steps in this area. Just a few days ago, the SEC Chairman Jay Clayton reiterated the agency’s position on classifying digital coins like Bitcoin as commodities while the Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and tokens given will be viewed as securities.
Similarly, Japan passed a comprehensive policy and introduced a self-regulatory body on digital currencies that make it a legal tender where exchanges are allowed as long as they are registered with the Japanese Financial Services Agency.
As expected, giving the green light to such a fast-paced movement made Japan the number one trading market for a lot of networks, including Bitcoin that has more than a half of its daily volume traded there.
Were There Any Recent Cryptocurrency Losses?
While there are numerous positive aspects associated with cryptocurrencies, it is important to acknowledge the adage “numbers never lie.” It has been observed that people who engage in impulsive purchases of random cryptocurrencies during hype cycles often end up selling at the bottom of bear markets. Conversely, those who adopt a strategy of regularly investing in Bitcoin only through a strategy called Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA), tend to exhibit greater resilience, enduring market downturns more effectively.
Looking at such a terrifying number that accumulated in less than six months really makes one wonder if a potential investment is worth it. Unfortunately, there is no way to answer that question and be completely sure if the given answer is correct.
Those interested in purchasing cryptocurrency must find a reason to believe it will grow in value again. Of course, such a scenario is very likely. Just consider how Bitcoin lost almost all of its value in 2011 when its currency exchange was hacked. Even after that event, which undoubtedly tarnished the platform’s credibility, Bitcoin showed to the world it isn’t just one exchange but a decentralized network, bounced back and achieved unprecedented growth in value in 2013, 2017 and 2021. That’s correct, these hype cycles are 4 years apart, just like the halving cycles, mentioned above.
Thus, the fact that a vast majority of cryptocurrencies are experiencing a somewhat of an “identity crisis” that is killing their value should not make them a permanently unstable investment. On the contrary, seeing digital coins reduce in value should open doors for potential purchases while the prices are low.
After all, the only way to gain a significant return is to own something when it is trading low. Then, you simply wait for it to skyrocket and realize the gain by selling. As stated, however, every investor must find it within themselves to justify any involvement with the rapidly-changing spheres of cryptocurrencies!






