Disclosure: Privacy Australia is community-supported. We may earn a commission when you buy a VPN through one of our links. Learn more.
Complete List of Vulnerabilities for SMEs (2014-2024)
Small to medium businesses (SME) might like to think large corporations are the juiciest targets for cyber criminals. The sheer number of news reports makes it seem that only behemoth companies have had their privacy breached and secret information exposed.
The truth is that SMEs face the same security threats that their larger counterparts do. Unfortunately, these SMEs do not have the advanced cyber security apparatuses employed by larger organizations.
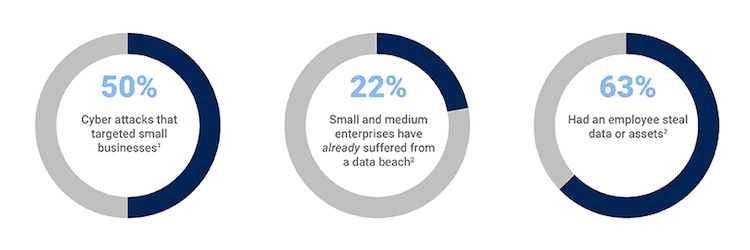
Here is a staggering number. In the United States, businesses with fewer than 20 workers account for 89% of all organizations with employees. And we just noted they are the least prepared to repel hackers.
In other words, small business has a big problem. Let’s take a look at exactly where theses threats come from.
Cyber Security Statistics SMEs

- Malware: In an independent study, 61 percent of small to medium size businesses represented in the study experienced a cyber attack during 2017.
- Spear Phishing: Phishing attacks resulted in the loss of billions of dollars by SMEs every year. Spear phishing is one of the greatest challenges IT departments face today and is the point of entry for many intrusions, including identity theft, ransomware, and hacking.
- Card Not Present Fraud: The incidence of CNC Fraud (aka “RFID skimming”) has increased over the past few years in both the U.S. and U.K. For example, the United Kingdom saw an increase from 750,200 reported cases in 2012 to 1,437,832 reported cases 2016.
- Lack of Cyber Security Knowledge: CFC UNDERWRITING, a cyber-insurance provider, stated that in 2016 approximately 38 percent of its claims could have been avoided if better education and training were implemented by SMEs.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service attacks can paralyze SMEs. In October 2016, 80 websites in the United States and in Europe were made inaccessible to the public because of DDoS attacks.
- SQL Injection: Sixty-five percent of organizations represented in an independent study said that they have experienced SQL injection attacks. These attacks got around their perimeter defenses putting their business at risk. SQL Injection was the 2nd most common form of cyberattack on WordPress sites – which power nearly 25% of the internet – according to a recent WP Scan report, and occur most frequently on outdated themes and plugins.
- Internal Attacks: Verizon investigated 500 intrusions that took place over four years. Their conclusion was that 18 percent of the breaches arose as a result of internal attacks. Although the number of internal attacks on SMEs are fewer than in larger companies, their impact is greater since in smaller companies individuals are given access to a number of systems.
- Awareness of Failed Cyber Attacks: A report published by the Sands Institute showed that 64 percent of respondents were unaware that they had been successfully/unsuccessfully cyber attacked.
- Cloud Service Securities Failures: In 2017, Chinese hacking group “Red Apollo” launched a global cyber espionage campaign that was unparalleled in its scale. Instead of attacking companies directly, it attacked cloud service providers and cloud networks to spread spy tools to a number of companies.
Small to medium size enterprises are vulnerable to cyber attacks because many of them feel that their size makes them an uninteresting target to hackers.
But as we’ve seen, their size and their lack of in-depth cyber security makes them a prime target for crooks. Large corporations are able to absorb the financial loss caused by cyber security breaches.
For small to medium enterprises, these breaches can mean that they are forced to close their doors. Let’s take a closer look at the seven vulnerabilities we mentioned.
Malware/Ransomware
Many small to medium enterprises are rethinking their business continuity and disaster recovery strategies because of an increase in malware and ransomware.
Ransomware encrypts files and then holds the files for ransom until the source behind the malware receives a fee.
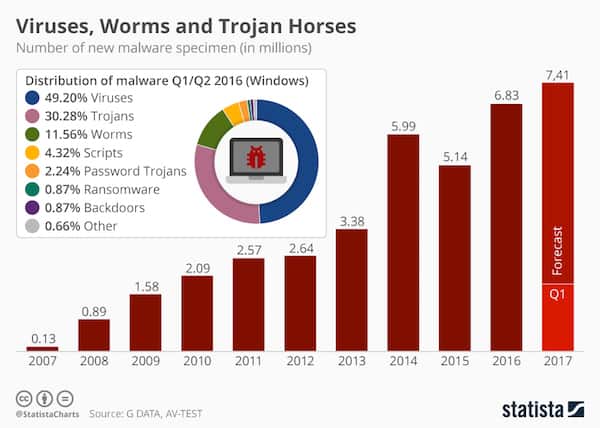
Ransomware spreads through phishing attacks, external network shares, and exploit kits. New strains of malware and ransomware are appearing online with such frequency that antivirus programs are unable to protect small and medium size enterprises.
Ransomware can work so fast that it can encrypt an entire computer within minutes of an individual clicking on a mimic email link.
An estimated 23 percent of SMEs say they do not have a recovery plan for restoring data that falls victim to malware/ransomware. Click here to learn more about malware/ransomware and how to protect your SME from it.
Spear Phishing
Unlike generalized phishing scams, spear phishing is targeted. Cyber criminals will use individually designed approaches, and they will rely on social engineering techniques to make an email seem legitimate and directed to the target.
Traditional security measures do not stop these attacks because of how customized they are.
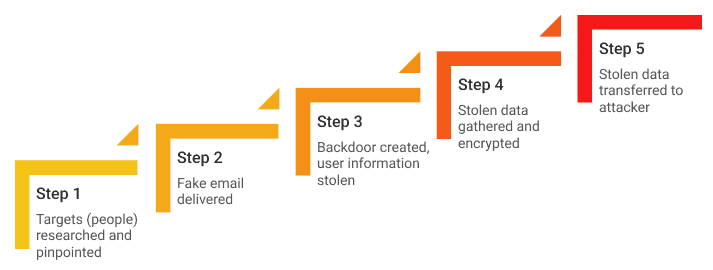
Just one slip-up is all cyber criminals need to deploy malware, employ denial of service attacks, and steal important data.
Even high-ranking individuals such as executives and management may find themselves opening an email they believe is safe, only to expose their company’s data. Learn more about spear phishing and how to protect yourself from it.
Lack of Cyber Security Knowledge
Reports show that low security awareness among employees is the leading cause of network insecurity. This has been the leading cause for cyber security breaches four years running. Surveys show that two thirds of US employees have never heard of ransomware or password protection.
It is unlikely that employees will take steps to prevent ransomware or other sources of cyber attacks if they do not even know they exist. Read this article to learn more about how cyber security knowledge can protect your small to medium size business.
DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are a nefarious tool used by criminals to disrupt the traffic of the server they target. The goal is to make the service or network so overwhelmed with a flood of Internet traffic that it becomes unusable.
DDoS attacks are effective because multiple compromised computer systems are used simultaneously to attack traffic. Cyber criminals can exploit your computer, machines connected to networks, and IOT devices.
During an attack, Internet traffic is jammed from a high level, which in turn prevents regular, desired traffic from reaching its destination.
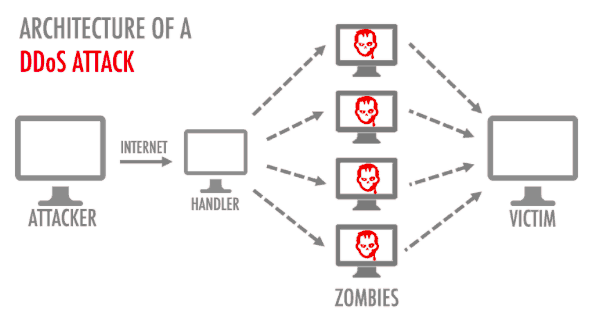
Your computer or other devices will be infected with malware. Each computer will become a zombie or a bot. A botnet is where an attacker has control of a number of network devices.
The attacker will target the IP address of their victim and cause the server or network to reach overcapacity. Since each bot is a legitimate Internet device, it can be difficult, if not impossible, to separate the traffic used in an attack from normal traffic.
This is a great resource to learn more about DDoS attacks and how to protect your small to medium enterprise from them.
For business owners looking to protect their websites from DDoS attacks please refer to my guide on the best Australian web hosts.
SQL Injection Attack
SQL injection attacks come in a number of varieties. It is a type of attack that can give cyber criminals total control over a web application database.
This is accomplished by inserting arbitrary SQL into a database query.
SQL injection attacks date back to the late 1990’s. Still, in 2019, they affect web applications around the Internet. The great news for SMEs is that SQL injections are easy to defend against.
They are not some state-of-the-art, CIA, unbreakable form of attack. It’s simple to fix your web application to minimize the risk of this type of attack.
However, there are some small business owners who have designed their own website or web-based application that have failed to do this.
Failure of this type is borderline gross negligence. Download this PDF to learn about the impact of SQL injection attacks and how to protect your SME from them.
Internal Attacks
Insider threats, be them from vendors, employees, or other individuals who have access to your data, are a potential way in for cyber criminals. The breaches could be caused by individuals who are negligent or those looking to attack your data with malicious intent.
Studies have shown that an increasing number of employees look to increase their income stream by selling their employer’s sensitive data.
The same study show that up to a third of employees stole their employer’s sensitive data or information as they were being fired or when they chose to start a new career.
They were using this information to start their own business endeavors or as a way to sabotage their employer.
Negligence has led to many individuals with insider access to their company’s files compromising the company from the inside without even knowing it. They clicked on phishing emails that gave criminals access to their company’s data.
As the threats posed by insiders increase, businesses are taking more action to protect themselves. These actions include:
- Employee training
- Incident response plans
- System monitors
SME owners often ignore or are oblivious to potential insider threats. This is why it is more important than ever that SMEs are proactive in the way they approach security and the way they search out insider threats.
Learn how you can protect your SME from internal attacks.
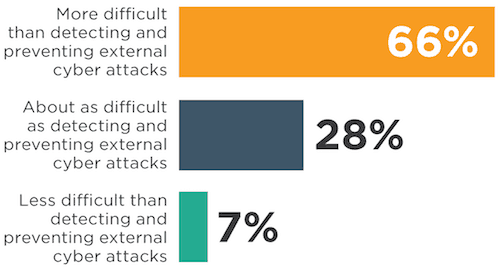
Awareness of Failed Cyber Attacks
Reports show that almost 65 percent small businesses in the United States do not respond after a cyber-security incident. Reports show that 70 percent of businesses around the world are not prepared for cyber attacks.
This vulnerability is disproportionately higher with small to medium size enterprises.
These businesses do not have strategies in place to prevent attacks, much less ward off attacks or detect them early if they do happen.
Although a substantial number of small to medium size enterprises say that cyber threats are their chief concern, half say that insufficient budget is the reason why they do not do more to protect from cyber attacks.
Improving cyber attack detection capability requires small and medium size enterprises to have ongoing monitoring of essential networks. Intrusion detection is also a must.
Tracking violations, whether they were successful or thwarted, incorporating monitoring, and manual logging can help to mitigate future risks. When it comes to cyber-attacks, ignorance is not bliss.
Cloud Service Securities Failures
SMEs are drawn to cloud service providers because of the flexibility and scalability they offer. Although cloud computing offers significant benefits and opportunities for SMEs, it also presents a number of security and privacy challenges.
Properly addressing the security challenges that exist in cloud environments requires a mixture of legal, organizational, and technological approaches. Unfortunately, much of this lies beyond the control or the financial limitations of SMEs.
There are a number of flaws in cloud architecture that offer the potential for cyber criminals to exploit vulnerabilities to security, gaining access to information that should be kept private.
Some of these challenges include a lack of control over data lifecycle, data breaches, and service hacking.
Cloud technology and cloud computing are relatively new technologies for SMEs to venture into. SMEs with a good grasp on business and an understanding of the appropriate steps to secure cloud technology can reap its benefits.
Click here to learn more about how cloud technology and potential security risks could impact future implementation.
Conclusion
SMEs face the same risks larger businesses do when it comes to cyber crime. Unlike larger enterprises, small and medium size enterprises usually do not have the financial backing needed to survive a cyber attack.
When a small to medium size enterprise experiences a data breach, they can quickly lose their customer’s trust. This is something that once lost is difficult to regain.
You can protect your small to medium size enterprise by first creating a plan of attack. Make sure that cyber security is a priority at all levels of your business.
Assign responsible individuals with the task of reviewing and maintaining the cyber security needs of your business. For individuals looking to protect themselves, opting to use the best VPN possible is your first and best choice.
Employees can be your best defense against cyber crimes or can be your weakest link. Train employees with cyber crimes in mind.
Use phishing experiments to see how aware your employees are of potential risks. Train new employees with cyber security awareness in mind.
Small businesses must create a plan for all incidents, whether they are successful or not. This plan begins with detection. It includes containment and notification.
Then, once the situation has been handled, it would involve an assessment of the way the company responded to the attack. Within this plan, there is no room for ambiguity. Each member of the team must have specific roles and responsibilities that are clearly defined.
For smaller businesses, outsourcing cyber security could be an effective way to increase preparedness. This does not relieve employees of responsibility.
Employers and employees must be aware and engaged. This is the only way to identify and protect small to medium size enterprises from cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
You May Also Like:



