Disclosure: Privacy Australia is community-supported. We may earn a commission when you buy a VPN through one of our links. Learn more.
Are Password Protectors Safe in 2024? List of Every Major Breach to Date

If you spend any time on the Internet (and who doesn’t these days?), then you probably have a lot of passwords.
You need a password every time you log on to your social media accounts, check your banking account balance or order something from Amazon.
If you belong to any forums, run a website or even just write a blog, then you have even more passwords.
It’s tempting to use the same password for each of these websites. After all, you probably need to sign in to dozens, if not hundreds, of websites during the course of a normal year. If you had a strong, unique password for each of these websites, how could you possibly remember them all?
Unfortunately, too many people take the easy way out. They use a password that’s fairly obvious, say “Password123,” for instance, and then use it for all of their online activities. Why is this such a terrible idea?
Because if a hacker manages to get your password on even one account, then they have your password for all of your accounts.
Maybe you don’t thing that it is a particularly big deal if some nefarious party is able to log into your Facebook profile, though they can wreak havoc if that occurs.
However, if that password gives them access to your banking information, your credit card numbers, SocialSecurity Number or anything else, then you will certainly care.
Why Strong Passwords Are Critical

In recent years, many websites have begun instituting requirements for increasingly long and complex passwords.
It’s a pain for the user to come up with and remember these passwords, but there is good reason for doing so.
The more complex and random your passwords are, the harder they are for hackers to discern. Now, imagine that you had dozens of these passwords, one for each of the websites that you frequent.
Those hackers won’t get as far when they have to figure out a completely random chain of 12 or more letters, numbers and special characters. The problems only get multiplied by your use of unique passwords on every one of your online accounts.
This type of password is critical to your online security. Once one hacker has figured out your too-simple password, they can use it themselves or sell it for major bucks on the black market.
Some of these buyers are incredibly sophisticated. Within minutes, your identity is stolen, your credit rating is trashed and you’ll spend years and lots of money trying to get your reputation back.
According to the MIT Technology Review, creating a truly strong password is about more than using one capital letter, one number and one special character. The longer you make your password, and the more special characters that it uses, the more likely you are to stump hackers.
Hackers have software that continuously and tirelessly runs through password “guesses.” Sooner or later, they may latch onto yours.
However, if your password is long, complex and totally random, then chances are good that the hacker will go looking for much easier prey, which is available in abundance.
What Is a Password Manager?
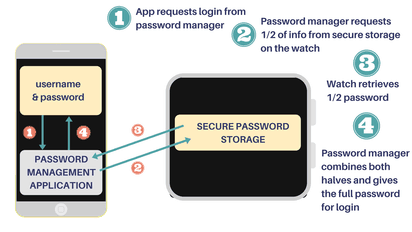
The problem is that remembering all of these incredibly long, complicated and unique passwords is a Herculean task. Who can possibly keep them all straight?
That’s where password managers come in.
Most password managers are designed to generate countless strong, random passwords for individual users.
They store these passwords, and then retrieve them when you visit each website.
It also is possible for these services to store your credit card numbers, including the three-digit CVV code on the back, along with PINs and your answers to various security questions.
All of these data are encrypted in a bid to foil hackers. Many of these services use hashing, which essentially is responsible for the conversion of plain data into strings of numbers or characters of a predetermined length.
Any time that you want to visit a website where you will need to use one of your passwords, you log into the “vault” of data that you previously stored with your password manager. Access is granted through a single password for the manager service.
That sounds pretty convenient, but it is critical that you do not put too much trust into password managers. These services are not a magic bullet that will protect you from all harm.
It is still wise to use a VPN like NordVPN for all browsing, two-factor authentication for certain extremely valuable accounts and to only use devices that you trust.
In fact, you might be wise to forego using a password manager at all.
Why Password Managers Can Be Risky 🔓️

Password managers store all of your sensitive data either locally or on a cloud.
Accordingly, your passwords are in a vault on a storage drive or computer at your home or they are kept remotely on the password manager’s servers.
Big-name players in the industry like Dashlane, 1Password, and LastPass use their servers to store your private information by default. This makes it more convenient for you to sync any stored data that you may have with all of your devices.
Now, these companies make a lot of promises about their security measures, but that doesn’t make all consumers comfortable.
Just imagine if all of that incredibly valuable data on that single server was compromised by a hack. Because you’ve put all of your eggs in one basket, you’ve just lost control of your online life.
The reality is that few hackers can resist the temptation to get past the advanced security systems. Think of all the priceless data they could gather with just one hack. Sometimes, consolidation is not a wise maneuver.
If you really dislike the thought of cloud storage for all of your passwords, then perhaps you could opt for local storage instead. Dashlane makes this possible when customers choose to disable the “Sync” feature.
1Password lets customers buy a software license that gives them control over where their vault is kept. KeePass makes it possible to store your data in a vault that’s encrypted on your own device.
However, before you jump in with both feet on these options, ask yourself how secure your own electronic security measures are? Is it possible that a hacker could get through them to take all of your passwords from your own device?
Security Breaches That You Need to Know About 🤔️

Security breaches are becoming more common. Since they are no longer a thing of the past, businesses of all types are having to take steps to beef up their security, including adding layers of defenses.
2021 has seen a lot of activity, some that proved just how sophisticated some hackers are getting when it comes to obtaining sensitive information.
Here are a few significant data breaches over the last three years, proving that no company (no matter how large) is 100% safe.
The Colonial Pipeline Breach of 2021
Instead of going after usernames or credit card information, attackers went after a major fuel provider, Colonial Pipeline. For the first time, their productions halted due to a ransomware attack launched by the infamous hacking group DarkSide.
When they breached the system, they halted production and got their hands on more than 100 gigabytes of data, sending a ransom to the company threatening to release information. This caused the gas prices throughout the US to spike, rising over more than six cents per gallon in some places.
At the end of it all, Colonial Pipeline was left to pay $2.3 million in Bitcoin for operations to continue.
The LinkedIn Data Breach of 2021
This year back in June, the accounts of 700 million users were impacted when hackers gained access to LinkedIn. The breach was not discovered immediately, with the usernames and location posted for sale on the Dark Web.
This happened more than a few times, with two separate uploads of data to sell, the first with 500 million user’s information and the second with 700 million.
Included with the data that was exposed were email addresses, usernames and profiles, social media account details, and more. Hackers exploited a vulnerability found in LinkedIn’s API, able to bypass security and obtain user and system information.
The CAM4 Data Breach of 2020
The CAM4 data breach happened in March 2020, impacting more than 10 billion records in the process. Some of the sensitive customer information that was exposed during this breach included full names, email addresses, IP addresses, and even payment logs.
This security breach was significant for a number of reasons, including the fact that many of the sacrificed emails were linked to cloud accounts, giving hackers the motive to launch aggressive attacks like phishing attacks in an attempt to gain access to more information.
Another reason dealt with the fact that CAM4’s content features adult video streaming, which resulted in defamation of many users whose names were exposed due to the breach.
The Facebook Data Breach of 2019
In April of 2019, more than 500 million Facebook users were impacted by the Facebook data breach. Hackers used to access data in third-party Facebook apps to gain access to user data, positing this information to the web.
This meant that entire Facebook profiles along with account names, likes and reactions, and more were exposed.
That was not the only time this breach come up, getting posted to the dark web a few years later in 2021. While many users had taken steps to change their account information to prevent additional exposure, some had not, resulting in increased chances of identity theft and more.
Starwood Marriott Data Breach of 2018
Back in November of 2018, it was discovered that the information of more than 500 million guests was sacrificed. Hackers were said to have gained access to the Starwood system back in 2014, gaining access to Marriott after its acquirement.
The information did not just include names and phone numbers but also included highly sensitive information like passport information and credit card numbers.
One saving grace for the hotel chain was the fact that all data was encrypted, and it was uncertain whether they had the ability to decrypt it to make use of it.
Ponemon and IBM’s Cost of Data Breach Report 2021
Each year, Ponemon and IBM team up to scour the web for key information and statistics about data breaches and online cyberattacks. The study attempts to find how companies were affected along with the total costs that go into patching up a breach.
Below, we’ll share some key insights into their findings, which point to one clear conclusion, the cost of a data breach is on the rise.
Cost of Data Breach Reached Record High 💰️
Data breaches are nothing new and have existed for decades. Over time, hackers have gotten much better at their craft, targeting some of the largest corporations and businesses on the web.
Though security is on the rise and advancing at a rapid rate, it’s still no match to put some of these breaches to a halt, with most resulting in costly repairs.
According to results, 2021 saw the highest average for a data breach as compared to data collected over the last 17 years, with a total of $4.24 million.
Compared to 2020, that’s a 10% increase, leaving a clear cause for concern. Among the industries that experience the most threat and the highest cost of a data breach are:
- Healthcare
- Financial institutions
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Technology
- Energy
What’s Behind the Cost?
A figure like $4.24 million is hard for a lot of companies to come up with. These costs can destroy a business, especially if they don’t have the funds to take action and start cleaning up the damages. While it might seem simple to find a reason behind the costs, some are confused as to where they come from and why they are so high.
According to the study, the number one reason behind the high costs is the loss of business. Taking a moment to stop and think, a lot of the biggest data breaches have hit companies that have had to completely rebrand themselves, basically knocking them down and making them start all over again.
Typically, when consumers hear that a business is not safe, they tend to avoid that business, as it has a permanent reputation of being a victim of a data breach.
Apart from the financial impact felt from the loss of customers, there was also a significant financial hit that went into detection and escalation of the attack.
Detecting an attack and getting to the root cause is expensive for several reasons, including that there is a need for a highly trained professional, and that productions have to halt while patches are being taken care of.
Last but not least, another impact came from costs post-breach, where businesses tried to get things set up and more secure than before. Not only do those costs come from additional security but also creating advertisements and incentives to regain clients once more.
An Evolving Work Environment
In 2020, there wasn’t a single person that was impacted by the pandemic. Even many who had a job were forced to work from home, making the internet a central part of it all.
While it might seem like a win for employees and companies, it actually increases the attack surface and makes it more sensitive.
Not only were companies rushing to create a secure infrastructure that allowed remote work but, many employees were taking it among themselves to work from their home network
Most home networks are not set up for advanced attacks, leaving experienced hackers more than enough space to play with.
The fact that working from home is on the rise and here to stay has created a need for companies to use security best practices when working on location or from home, ensuring that both employee and network are secured and safe.
Current Data Breach Facts to Be Aware of 📑️

Any person or organization online, especially those who deal with customer data, must have a solid security system.
Even if they do, there are key things that they should be aware of, understanding what kinds of threats they’re facing when they get online.
Detection is Taking Longer
If there is one threat that all those on the internet should know about, it’s the fact that detection is taking much longer than ever before.
Even with monitoring software, some attacks are sneaking into systems via browser-side or client-side, even harping on the IP address via a man-in-the-middle attack.
The longer an attacker is left undetected, the more damage that they can cause, even making multiple trips to access more data and obtain more information about accounts. While some are detected automatically, others could take months or years to detect.
Containment is Taking Longer Too
Another threat to be aware of is the fact that some attacks that result in sacrificed data can take more than 300 days to contain. That means that from the time of detection until the breach is patched and accounts are safe once more can take close to a year to straighten out.
Most data breaches that take that long deal with compromised user credentials, as they have access to more than just one set of data.
Incidence Response is Life Saving
It’s not just about patching a data breach and moving in. Companies also need to have a plan to keep things from happening again. That’s why incident reporting is lifesaving, allowing companies and other organizations to refer back to breaches and decrease their response time.
An incidence report is not something that saves time and money right away but is something that helps out a lot in the long run, helping companies keep track of their overall system health and their chances of an aggressive attack.
What’s the Future Look Like? ➡️

If there is one thing to be hopeful about, it’s the fact that developers and security gurus are hard at work developing the next biggest things.
Today’s aggressive attacks and expert techniques used by sophisticated attackers are no match for outdated security measures, which is why the future is sure to see innovation and evolution.
Automation and AI
The powerful team of AI and automation is making the detection of suspicious activity easier than ever before.
Now, companies can add software to their system that scans, monitors, detects, and even alerts when something isn’t right. Instead of leaving IT professionals to hunt for activity all day, they are alerted where the problem is, able to get there, and check it out to reduce response time and potential damage.
Blended Protection 🛡️
There are a lot of companies out there already using this technique, and it’s expected to increase in the very near future. Blended protection is a technique that takes different types of security and placed them throughout the network, attempting to detect issues that could happen at different layers.
This could be a firewall, a monitoring software, an automated tool that patches and reports, and a database of attacks and solutions all in one. The key is to protect the system from the outside all the way to the most inner space to prevent attacks of all kinds. Attackers will exploit whatever they can, no matter which layer they find a vulnerability in.
Quantum Computing
It’s not as intimidating as it sounds but quantum computing is opening the doors for all-new ways of protecting systems and networks. Using these powerful machines, IT professionals are mimicking the most popular attacks and used by hackers, allowing the computer to learn and create scenarios for solutions and more.
Some of the scenarios these computers are exposed to are very complex and, over time, it’s a goal to have software that detects event the slightest changes that in a system that hackers are attempting to breach.
Advancements to Current Security Measures 🔒️
Even though things like firewalls and password managers have been around for some time now, they are too good to throw out. Instead, IT pros are making them better than ever before, giving them advanced features, and making sure there are no bugs in them that can sacrifice a system.
A lot of companies are keeping some of these technologies and using them as part of their entire data breach prevention setup, able to detect suspicious activity from the inside out.
You May Also Like:



