Disclosure: Privacy Australia is community-supported. We may earn a commission when you buy a VPN through one of our links. Learn more.
What Are Blue-Chip Stocks?

The phrase “blue-chip stocks” emerged from the velvety James Bond world of poker, used as a reference to the different colours designating chip values. Blues usually have the highest value, greater than red and white chips.
In this way, blue-chip stocks are considered to be the most stable, well-established companies in an industry and ones that are viewed as safe and reliable investments.
Such companies tend to have a track record of profitable operations, strong balance sheets and wide market recognition. As with any type of stock investment, before you buy blue-chip stocks you need to do your research — as with poker — there’s always an element of gambling.
However, when it comes to long-term investing, blue-chip stocks may be the perfect fit for your portfolio. In today’s guide, we cover how they work.
Table of Contents:
- 🤵 What are Blue-Chip Stocks
- 🔵 History of Blue-Chip Stocks
- 🔵 Measuring Performances of Blue Chips
- 🔵 Advantages of Blue-Chip Stocks
- 🔵 FAQs
What are Blue-Chip Stocks? 📘
A quick disclaimer: we offer summary guides to important topics. They are not definitive, and this isn’t financial advice. We provide you Mission-critical data efficiently. It’s up to you to do your research and make sure it relates to your specific context. Below, we’ve listed a few things you should know about how blue-chip stocks work:
- ✔️ Prodigious reputations. Blue-chip stocks represent enormous companies with long-standing track records, often with some of the world’s largest household names.
- ✔️ Can be used for retirement. Investors in the past have frequently been people with steady finances looking to secure dividends.
- ✔️ Robust and resilient. There is a viewpoint among investors that blue-chip stocks are able to survive market threats of many types; although there is truth to this, it is not guaranteed. This is why some recommend diversifying further than this.
- ✔️ Industry-leading. Needless to say, blue-chip stocks are the best companies in their industries, the most well-known, best capitalised, with the most stable financial forecasts — but the list does change from quarter to quarter.
History of Blue-Chip Stocks 🏛️
Blue stocks were originally issued by industrial companies as a way to raise capital.
They were typically highly stable stocks that were able to pay dividends and maintain their price despite fluctuations in the market. These stocks were typically traded on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE). The blue-chip idea for stocks came about during the Great Depression. Investors were seeking stocks that were reliable, consistent and could be counted on to stay in business.
Companies that had a reputation for being a “blue chip” stock were able to raise capital by issuing more shares at a lower price as investors were willing to pay up for these shares, as they were deemed to be safe. Blue-chip stocks were also used as a way to raise capital in the late 1800’s and early 1900’s. Investors would purchase shares of companies that were considered “blue chips,” as they were thought to be more stable than other stocks.
Rise in Popularity
At the time, investors believed that these companies would have a better chance of surviving than other corporations because they could be counted on to provide high returns, which helped them in their quest for wealth.
The blue-chip stock idea took off during World War II when investors began looking for a safe investment opportunity. They felt that if the United States was going to continue fighting in the war and facing an onslaught of enemy planes, it would be better to invest in these American-made products rather than foreign ones.
In addition, investors wanted to earn a return on their investment because they believed that an American company would have greater financial stability after war was over and prosperity had returned.
During the 1930s and 1940s, blue-chip stocks became popular due to the fact that they were considered much safer investments than other investments such as bonds or real estate. By this time, people began looking for cheap investments and holding blue chips instead of any other type of investment such as stocks or bonds because it was thought that investing in these companies would give you greater returns over time.
Measuring Performances of Blue Chips 📐
Blue chips were once reserved for well-off boomers, people with high net worth is at a time when property was cheaper and the living wage was much greater. Financial advisers managing portfolios of his clients track the performance of blue chips using chart patterns and referring to the different indexes.
In fact, the Dow Jones is often used as a measure of the health of the American stock market in sum. However, it is only an index for America’s leading blue-chip stocks. Other economists regard the Dow as too curated. This is because it only tracks 30 firms, which arguably does not adequately reflect the fuller market.
By comparison, the S&P 500 — would you guess — is comprised of 500 firms. However, the largest 10 companies represent roughly 27% of the market capitalisation. Among these are what is termed “dividend aristocrats,” because these firms have reliably issued dividends for at least a quarter of a century.
For Australia, of course, is the ASX50, representing the 50 leading companies in Australia. And the FTSE 100 for UK. Among others. The NASDAQ 100 represents one of the biggest indexes for non-financial firms, one of the lists in this is “FAANG” — this represents the most dynamic blue-chip companies in that index, names like Netflix, Amazon, Facebook (Meta), Apple, and Google.
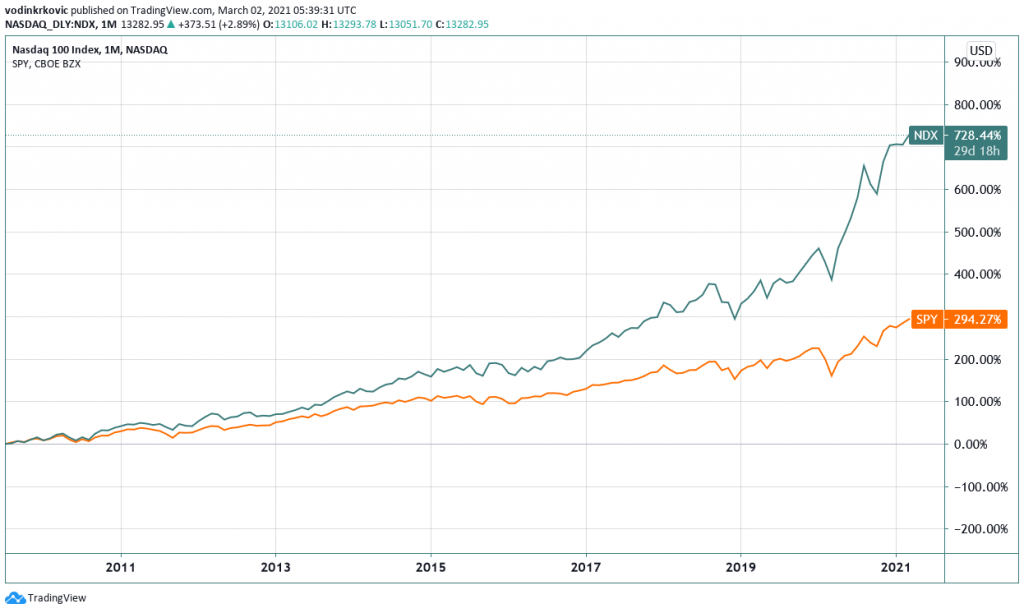
Chart representing the total returns for both the S&P 500 and NASDAQ 100 over the last decade.
Each index has its own advantages. And which one you choose will depend on your investment strategy. For instance, investors seeking higher growth would probably dip into the NASDAQ 100 – to pick out one of the more dynamic blue-chip stocks not related to finance. Whereas someone looking for stable dividends would focus on S&P Aristocrats.
Advantages of Blue-Chip Stocks
Blue-chip stocks are often associated with strong brand recognition and have a large number of assets that are hard to liquidate. Because of this, they are more likely to be able to weather the ups and downs of the economy and continue paying dividends to shareholders.
Although they come with lower rates of return, blue-chip stocks are often included in retirement savings plans since they are seen as low-risk. Blue-chip companies are often more conservative in their approach to business, which may make them more resistant to cyclical downturns in the economy.
The stability of blue-chip companies can make them attractive investment choices, particularly during times of economic uncertainty. Blue-chip companies often pay higher dividends than other stocks, which can be attractive for long-term investors.
Blue-Chip Stocks as a Safe Investment:
- 👑 Blue-chip stocks tend to be traded by large, well-established companies. As such, they are less likely to be affected by economic forces, such as interest rate changes, that can cause stocks to greatly fluctuate in value.
- 📊 The stability of blue-chip stocks can be an attractive draw for investors who are looking to diversify their investment portfolio.
- 📈 Blue-chip stocks tend to be less volatile than other stocks, making them a relatively safe option when it comes to investing in stocks.
How to Find Blue-Chip Stocks
There are a few different ways that you can find blue-chip stocks in your investment portfolio. You can search for stocks that have held their reputation as a blue-chip stock over many years, or you can look for stocks that have recently become blue-chip stocks, such as Tesla.
Investors can buy individual blue-chip stocks your direct market access (DMA). For this, you use an online trading broker and open up a position on a particular stock, for instance, shares in Amazon (AMZ) stock. In other cases, the various kinds of funds (index, mutuals) and exchange-traded funds offer an assortment of stocks and various asset classes, with blue chips among them.
You can also choose an ETF or other type of fund, for instance, an index fund that exclusively focuses on blue chips, such as investing in an ETF that tracks the S&P 500, which comprises 500 of the largest blue-chip stocks.
What Makes Blue-Chips: Parameters Explained 🔵
The hall of fame blue-chips are very obvious. You have the likes of Coca-Cola, Starbucks, Berkshire Hathaway, Amazon, Apple, and Microsoft. But it’s harder to spot the dividend aristocrats and other blues that lie away from the starlight.
In order to identify them, we can gain a little bit of guidance from an investment professor, Janet Lowe, who discusses some of the key characteristics of companies in this realm:
1. Dividends have increased five times in the last 12 years: increasing dividends represent a few things. Firstly, it demonstrates that a company is happy to share its success with its shareholders. Secondly, it’s a signal that a company is organised enough to perform reliably across time. In a way of saying this is that blue-chip companies are like rare materials.
2. Broad market capitalisation: large market capitalisations imply strong liquidity and it safeguards that stock to some degree against pump-and-dump schemes and other market manipulations of the stock value. As with Elon Musk buying Twitter, however, we have seen that it is by no means impossible for an individual investor to have an immense effect on the market.
3. Supported by over 80 organisations: not a globalist statement, but you have to recognise where the money is going and it’s easier to go downstream than upstream. So the investment wisdom is, if you can’t beat them, invest in them. Institutional investment managers want to keep an eye on — these guys head portfolios for mutual funds, retirement packages, banks, building solutions, and the rest. They are responsible for making sure portfolios are comprised of high-quality stocks. It often pays to know what the institutions are focusing on. According to some experts, the safest blue chips are those where a minimum of 80 institutions on 50% of outstanding shares.
4. Seven or more of the last 12 years saw increasing earnings: some investors view blue-chip investments as like a marriage. Investors want to ensure that they are committing to something that can survive economic turmoil. They expect periods of chaos, but they want to know that the blue-chip company can hold out in the long run.
5. At least 25 years of consistent dividends: generally speaking, the company matures into blue-chip status once it has matured beyond ¼ of a century. Which means, the order and more reliable companies were been paying dividends for a longer period. One such example is Stanley Black & Decker, which has offered dividends for over 140 years and has even increased dividends each year since 1968. Hard to ignore.
6. At least an “A” ranking: the Standard and Poor’s (S&P) grading system works in a similar way to your credit score. The better the grade, the more that the regulators believe this company is able to honour its financial commitments.
When you decide which blue-chip stocks are best for your portfolio, make sure that you’re reviewing their market capitalization and how they fit into your investment strategy.
When you’re researching blue chips, make sure that you’re looking at the company’s stock performance over several years. I suggest you look for companies that have a strong track record of increasing their dividends and expanding their operations. If you want to invest in blue-chip stocks and don’t have time to go through all the research, then I recommend using Craig’s List or Yahoo as your search engine.
You want to make sure that the companies you’re investing in are large and stable enough to weather any economic changes, while also having a track record of reliably paying dividends to shareholders.
More than 25 million people use eToro. This platform dominates the social trading market, letting you work with experienced traders and mirror their positions. This platform lets you open up a demo account, that you practice with £100,000 — in a virtual portfolio… For more, visit etoro.com/trading/fees.
☑️ How the stock market works (and blue-chip companies)
The market for stocks is based on a combination of supply and demand. The price at which a company purchases its stock is called the bid and ask price. The bid and ask prices are set by the investment banks that oversee the market for stocks.
They then set a floor price at which a company is willing to pay to buy its shares from another company. This floor price will be determined by several factors including:
- An industry’s size
- A company’s level of profitability
- The number of shares outstanding per share (share count)
☑️ The costs of investing in blue-chip stocks
Investing in blue-chip stocks is generally associated with low risk, but it also doesn’t come with the potential of high returns through aggressive growth stocks.
Blue-chip stocks are often viewed as being a “safe” investment. While this is often true, one of the downsides of investing in blue-chip stocks is that they may not be the best option if you’re looking for a high rate of return on your investments.
If you’re looking to maximize the amount of money you make on your investment, blue-chip stocks may not be the best option. Blue-chip stocks are often associated with having a lower rate of return, but they also come with lower risk. If you’re investing for the long-term, blue-chip stocks may be the ideal choice for your investment portfolio.
Blue-Chip Stock Dividends 💸
You’ve made this section because the majority of blue-chip companies pay decent dividends. For that reason, it’s important that you know how to use your dividends. If your initial investment is great, this can lead to a large number of passive returns. But most of us won’t be quitting our job just yet and will need to trickle more funds in over time.
One way to do this is through something called a DRIP, or a dividend reinvestment plan. This program gives shareholders the right to automatically make the dividends buy more shares. This means shareholders continue to drip more money into the blue-chip, in order to get a bigger return on investment on the stock later on — rather than cashing in right away.
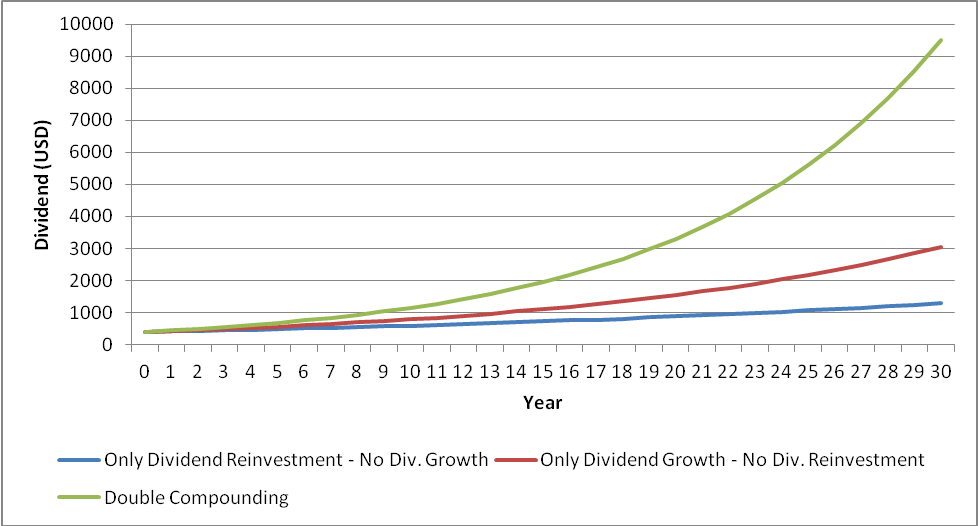
Table representing compound dividends of AT&T over a decade.
To explain the trip, let’s use the AT&T example illustrated above. Suppose you purchased three shares and chose to automatically reinvest dividends, as well as an extra £100 every quarter. Over a decade, you would be at 229 shares and more than £600 in dividends.
Funds for Blue-Chip Stocks 🗂
Exchange-traded funds have many advantages as a way of investing in blue-chip stocks. One of those perks is ETFs being later to the game. Like the younger son in the family, these dinner pop up until the 1990s, so had more time to mature based on a broader context.
Index funds and mutual funds have a similar nature to ETFs, in that they innately have a certain amount of diversification. We are naturally lower in risk than purchasing individual stocks — based on probability. The essential difference however is that ETFs have lower fees and get traded in a similar way to stocks because they are under passive management.
But for greater dividend ROI, investors might want to go for individual stocks instead. This is because — despite the fact that ETFs are only passively managed — it does still come with a management fee. These fees do not come with individual stocks. So investors who have strict budgets may opt for some of the cheaper blue-chip stocks under £20 apiece.
Performance of Blue-Chip Stocks During a Recession 📉
Blue-chip companies may be recession-resistant, but this does not mean they are recession-proof. The sessions, like the one we are seeing in Australia in a very intense way — which popped its head up during the 2018 crash and the coronavirus pandemic — it can affect even the bluest of companies.
Historically, it’s clear that recessions affect how stocks are priced more than dividends. But dividend growth can still be impacted by depressions and recessions. The pandemic is another example of this, when almost 500 companies on the London stock exchange had to either suspend or permanently remove their dividends.

Surprisingly, bond yields were not affected greatly. But the Oracle of Omaha, Warren Buffett, believes that things will grow far worse for bonds. We have already seen a lot of chaos in that area.
FAQs 📘: What Are Blue-Chip Stocks?
What Companies Are Considered to Be Blue Chips?
Blue-chip companies are some of the most well-recognised, household names on the planet. But they are also lesser-known companies, that only people in the industry might be aware of who have provided long-running services at the highest level — many of these will have provided dividends for at least 25 years, with the last 12 years increasing, and have lots of institutional funding. You can find these blue chips in indexes like the FTSE 100, Dow 30, S&P 500 — names like Tesla, JP Morgan Chase, Black & Deckers, and Walmart.
Where Does the Term “Blue Chip” Come From?
From a smooth world of James Bond and poker-playing gamblers. The value of a chip at the poker tables is designated by its colour. Blue is typically the highest on the table, more than white and red chips.
Are Blue Chips a Good Investment?
A diversified portfolio might include some portions of blue-chip stocks, which means stocks of very well-established and reputable companies that the market understands deeply. This can be done in many ways, by purchasing stocks outright or investing in a mutual fund, exchange-traded fund, or index fund.
Are blue chips safe, why are they stable? No stock is 100% guaranteed. But they are safer than the majority of stocks because they have fewer liabilities, bigger customer bases, more capital backing them, greater institutional support, and are more likely to be bailed out by the government
How Should I Invest in Blue Chip Stocks?
Find a safe broker who has access to the markets that you want to be exposed to. And choose your investment route. There are many combinations that you can choose from. For instance, one ETF might have a rasher of blue-chip stocks. While another focuses exclusively on blue-chip stocks tracked from the Dow Jones industrial average, the London stock exchange, etc.
Are Blue-Chip Stocks Worthwhile?
Blue-chip stocks can be a very powerful part of a long-term investment strategy. Because of their high price, it might be tricky to buy them outright — younger investors will probably struggle more.
How Many Blue-Chip Stocks are There?
No definitive list for all blue-chip stocks exists. Which is why different experts use different rules from the classify what should fall into the category. The majority of blue chips on the Dow Jones Industrial Average (30 of America’s biggest companies) rank among the most important blue chips. In general, these will be well-known, older companies that everybody understands well and have proven themselves capable of resisting recessions.
How Can I Purchase Stocks that Pay Dividends?
Buy for your broker, as per normal. Those on the Dow Jones industrial average and the S&P 500 aristocrats are a good bet.
Conclusion 🌞
Blue-chip stocks are often associated with large and well-established companies that represent a safe investment. It can take a long time for a stock to become a blue-chip stock, so it’s important to choose wisely when deciding what stocks to invest in.
It’s also important not to become too complacent, as blue-chip stocks tend to be less volatile than other stocks, making them a relatively safe investment. But they move slowly.
You Might Also Like:






